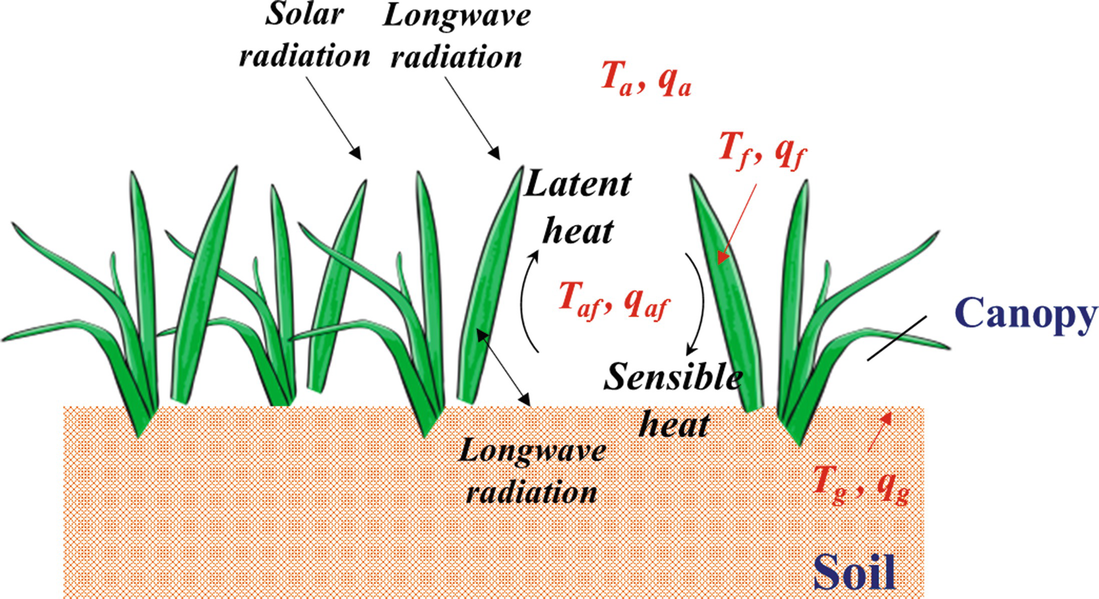
Traditional roof green roof n sensible et r q q q substrate 0 where r n net radiation q sensible sensible heat flux due to convection q et latent heat flux due to convection q substrate roof conductive heat flux through roof n sensible r q q roof 0 energy balance.
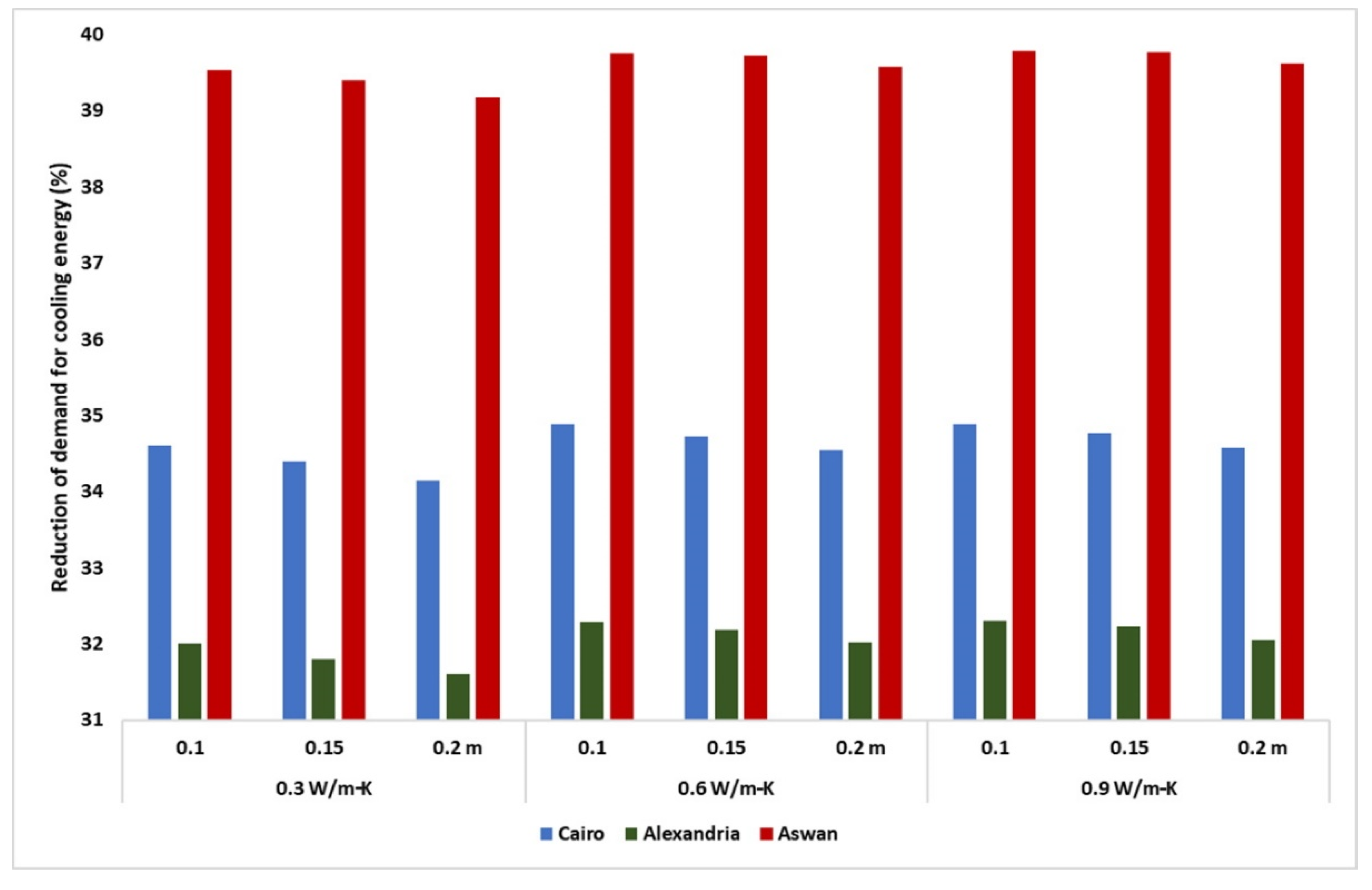
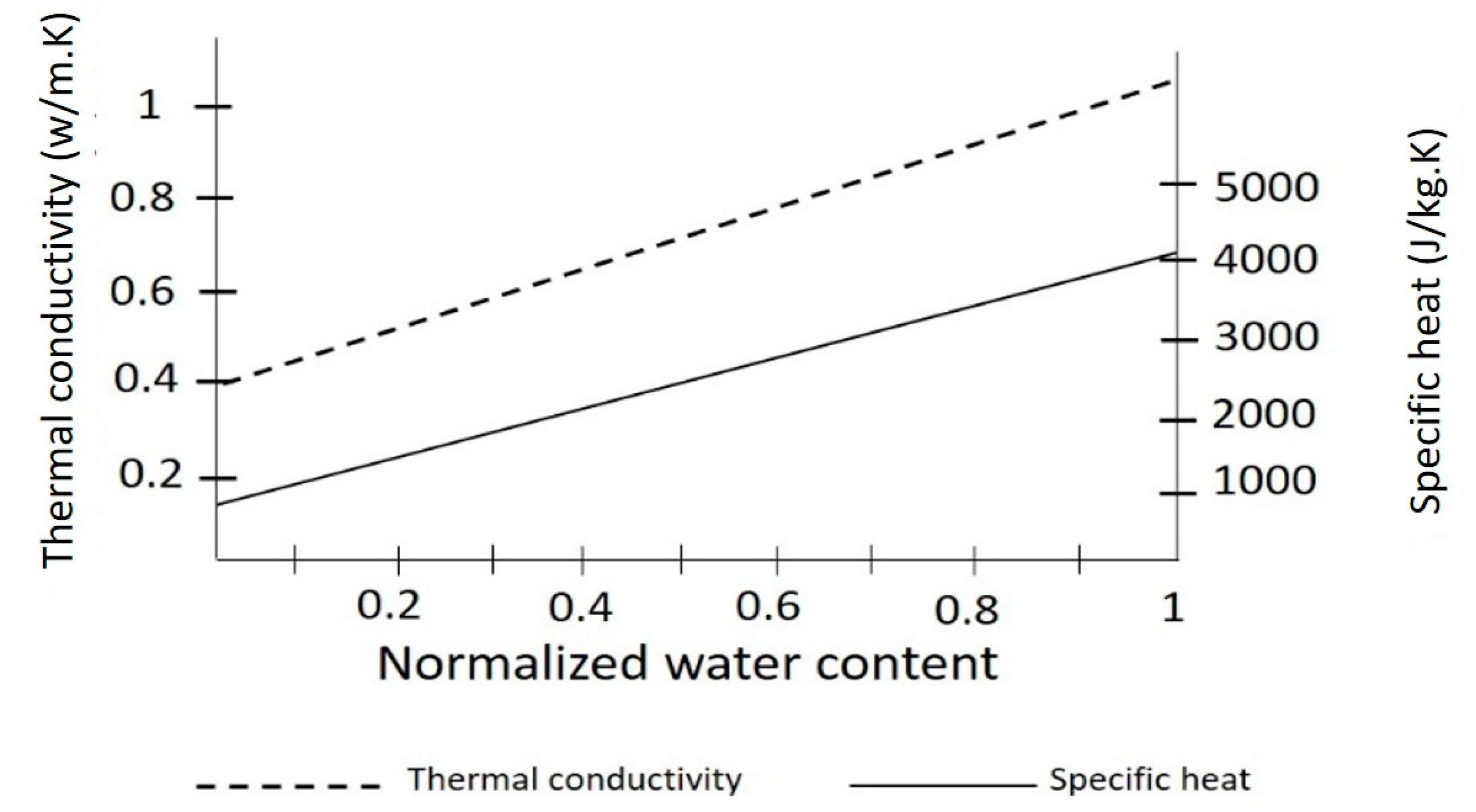
Green roof soil thermal conductivity.
In present study f is the thermal conductivity of air as a fluid component of a dry soil.
For the acob analysis the soil was considered to be fairly saturated at the bottom of the soil layer where the soil analysis was done.
Green roofs with silt clay soil required more than twice the amount of soil moisture than green roofs with sand to achieve similar roof heat transfer rates.
8576 𝜅2𝑃 𝑓 1 𝑓 1 𝜅2𝑃 1 1 1 where s and f w mk are the thermal conductivities of solid and fluid phases respectively.
The study concludes that green roofs can lower thermal losses.
Conductivity of green roofs bioresources 14 4 8573 8599.
The best net heat flux gains for vegetated green roofs were 4 7 w m 2 for the sand roof and 7 8 w m 2 for the silt clay roof.
The thermal conductivity for soil was only used on the acob roof analysis since the uppermost sensor used on the green roof analysis 2bn was sitting in 1 5 inches of soil above the surface of the ceiling.